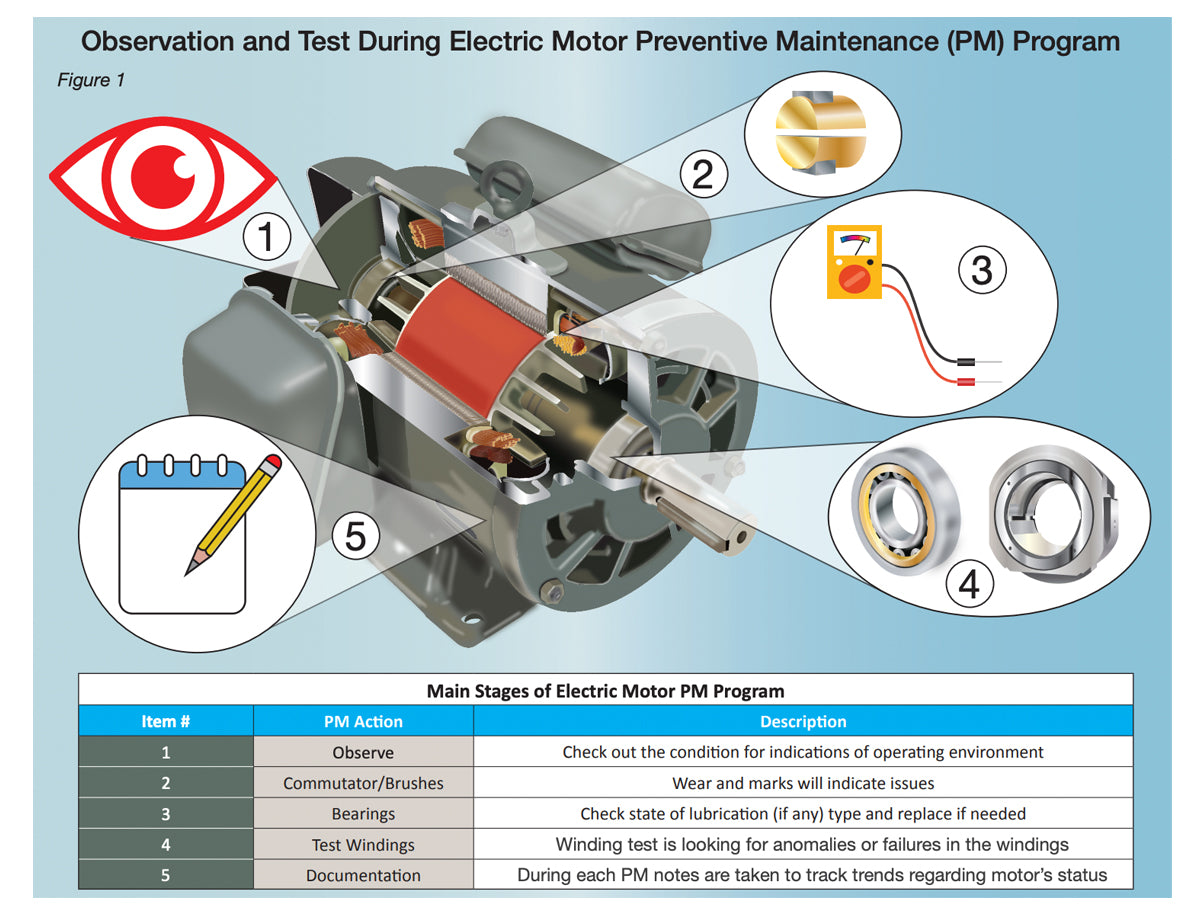
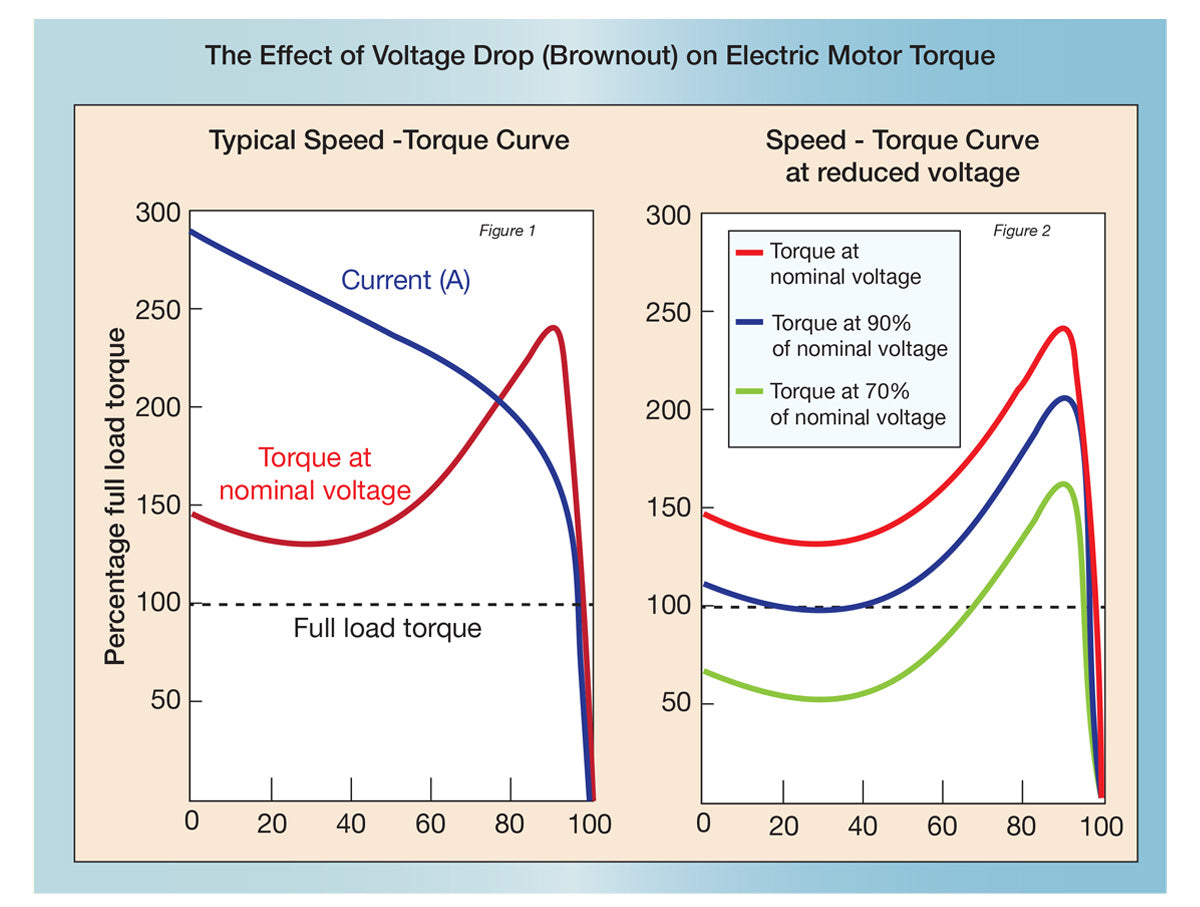
Information Sheet #7 - Variable Frequency Drive Applications & Explanations.
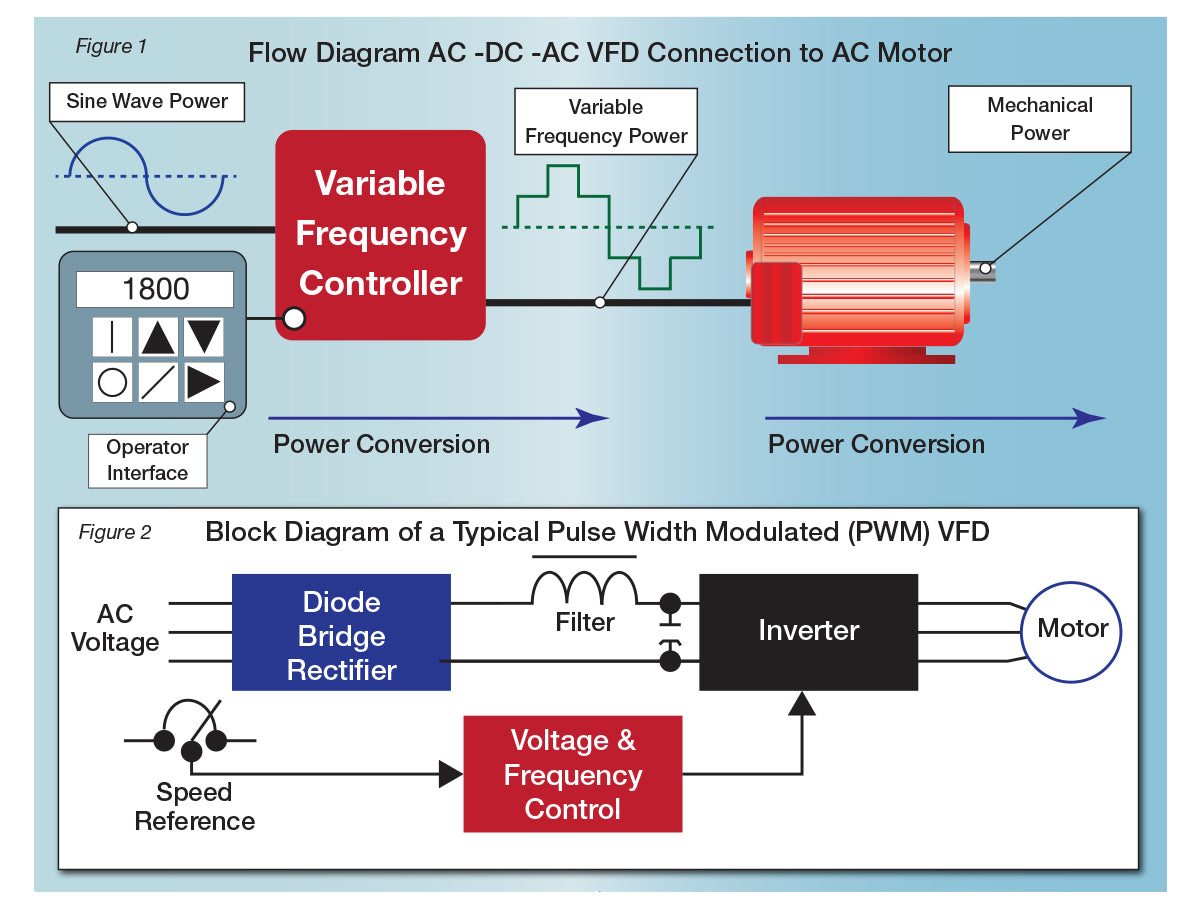
1.0 Introduction:
Variable Frequency Drive, usually using the acronym VFD, refers to the technology for fine control of motors with an electro-mechanical drive system. VFD has two principal benefits, first a more efficient way to start and ramp up an electric motor, and secondly a method for finely controlling motor speed and/or movement with a wide range of systems, including but not limited to, continuous manufacturing process, industrial and commercial machinery and water-treatment plants. While the technology is not new, the advancements in digital switching technology has greatly accelerated the use of the VFD.
2.0 Explanation of VFD Technology:
The primary purpose of a VFD is precise control of electric motor speed. With a VFD, a system designer can precisely control ramp up and ramp down speed to ensure all the components within a process are coordinated and operate efficiently in sync. Without a VFD an AC electrical mechanical device, such as a constant electric motor, just runs up to constant speed as current is applied and while doing so consumes up to 7-times the running amps required, to overcome starting torque. Prior to the application of VFD, motors would have to be connected to various mechanical components such as gears.
Also in Information Sheet Blog
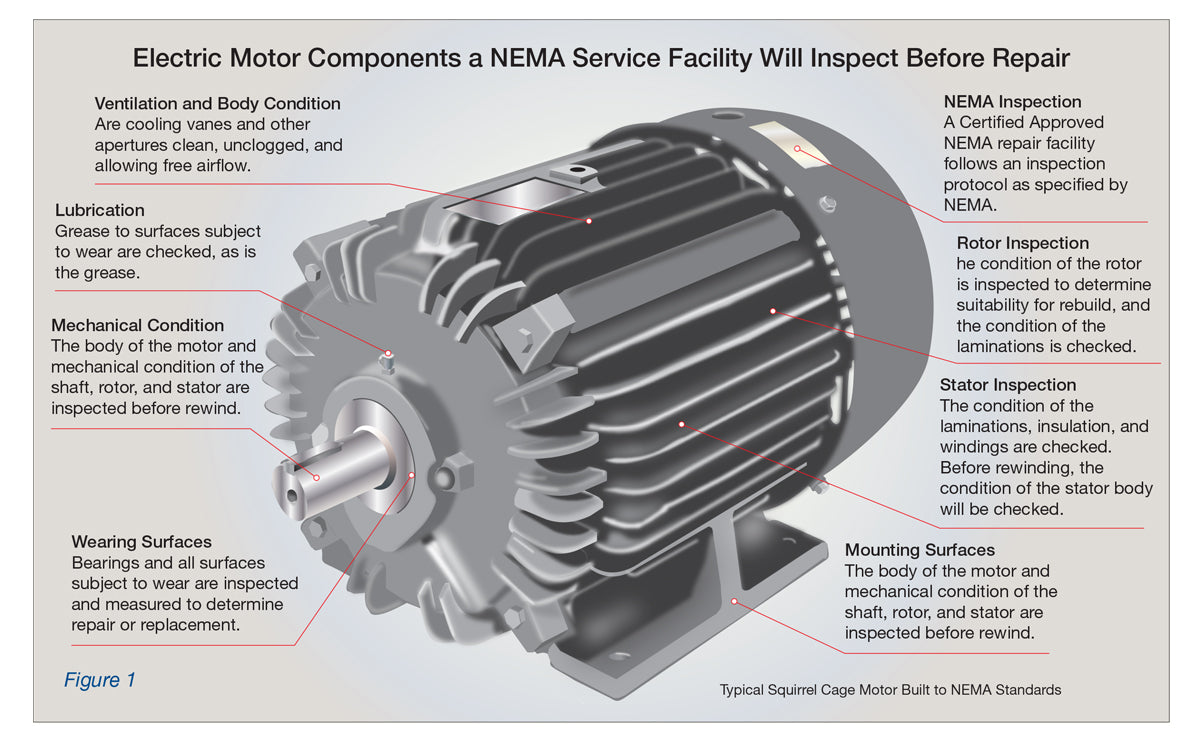
Information Sheet #13 – NEMA Motor Repair, Best Practice & Definitions